JAVA LOCK
面试题:用两个线程,一个输出数字,一个输出字母,交替输出数字和字母。
核心是交替输出,就需要两个线程之间进行通信。
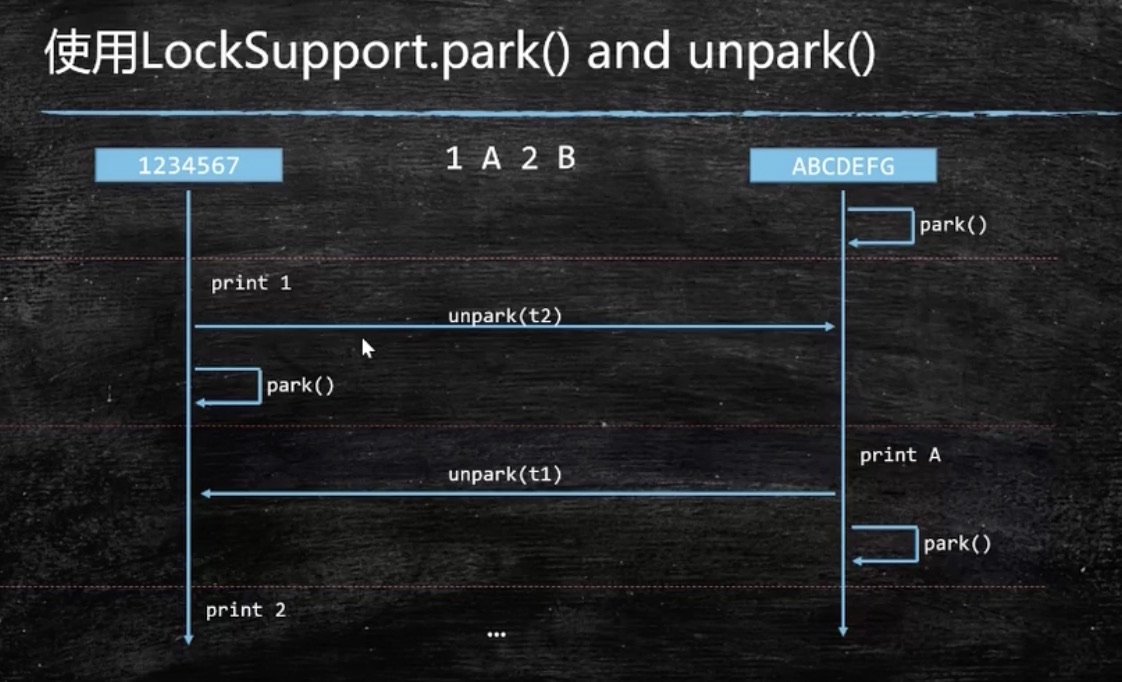
使用 LockSupport 实现
public class LockSupportTest {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] chars1 = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : chars1) {
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t2); //叫醒 t2 线程
LockSupport.park(); //当前线程阻塞
}
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : chars2) {
LockSupport.park(); //当前线程阻塞
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t1); //叫醒 t1 线程
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
T2 线程上来先阻塞,等 T1 线程打印第一个数字后,再叫醒 T2 线程,然后 T1 自己阻塞,等待被 T2 叫醒。
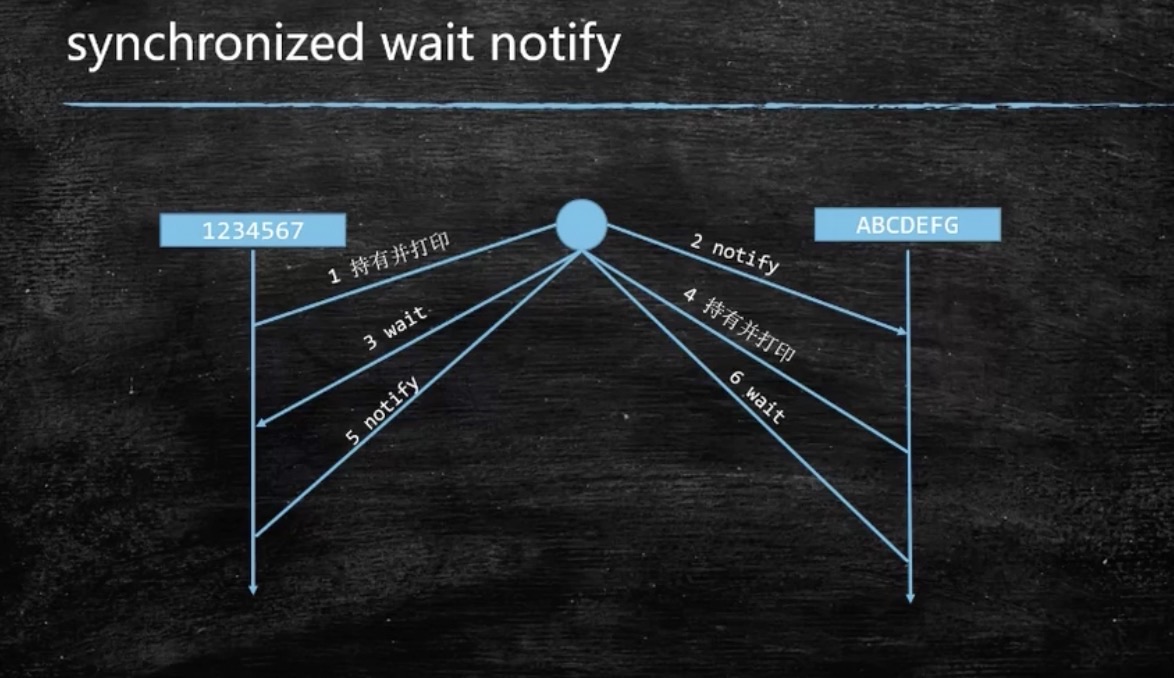
使用 synchronized wait notify 实现
public class SyncWaitNotify {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
char[] chars1 = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : chars1) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify(); //通知其他线程
o.wait();//自己阻塞,让出锁
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify(); //必须有这个句话,否则程序无法结束
}
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : chars2) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify();
o.wait(); //自己阻塞,让出锁
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify(); //必须有这个句话,否则程序无法结束
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
有一个线程先获取到锁,假设先获取到锁的是 T1 线程,打印出第一个数字后,通知其他线程,并自己让出锁,这是 T2 线程可以获得锁,获得锁后,打印第一个字母后,通知其他线程,并自己让出锁。
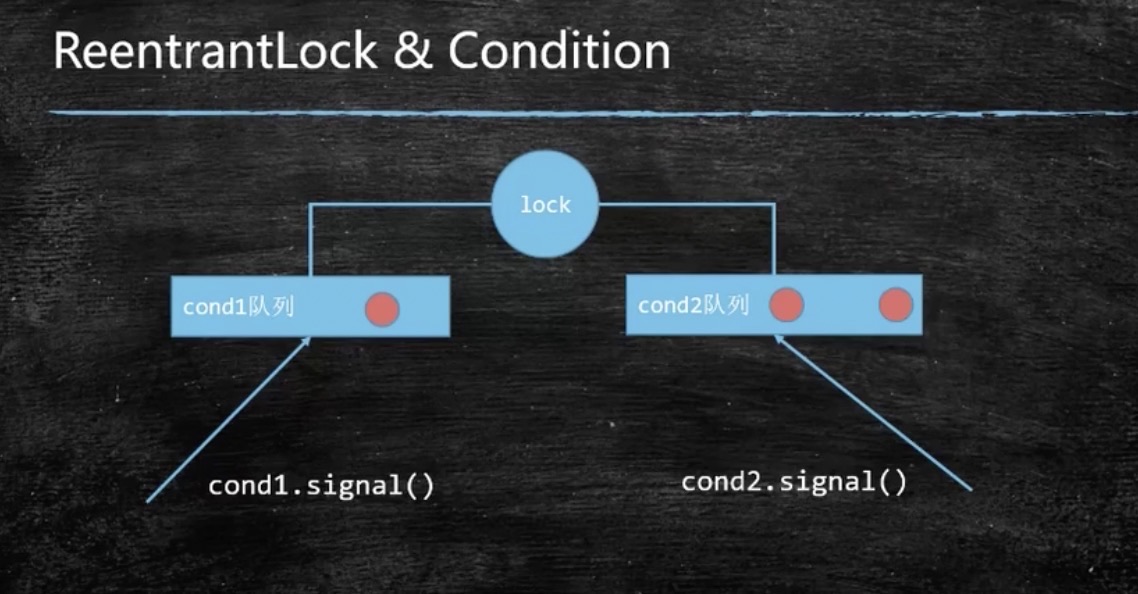
使用 ReentrantLook 可重入锁实现
public class ReentrantLockTest {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] chars1 = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 相当于是一个队列
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock(); //相当于是 synchronized
try {
for (char c : chars1) {
System.out.print(c);
condition.signal(); //相当于是 o.notify()
condition.await(); //相当于是 o.wait()
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
for (char c : chars2) {
System.out.print(c);
condition.signal();
condition.await();
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
使用 TransferQueueTest 实现
public class TransferQueueTest {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] chars1 = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
TransferQueue<Character> queue = new LinkedTransferQueue();
t1 = new Thread(()-> {
for (char c : chars1) {
try {
System.out.print(queue.take());
queue.transfer(c);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t2 = new Thread(()-> {
for (char c : chars2) {
try {
queue.transfer(c);
System.out.print(queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}